|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GRID-LAYOUT | ||||
|
|
||||
|
Das Layout mit dem “pack”-Mechanismus ist nicht immer leicht zu verstehen. Deshalb gibt es seit Jahren einen Nachfolger: das Grid-Layout. |
||||
|
|
||||
| Structure | ||||
|
The structure of a grid-dialog are different than a pack-dialog: |
||||
|
|
||||
| 1. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
n=5
for rownr in range(0,n,1):
for colnr in range(0,n,1):
bn = tkinter.Button(root)
bn["text"] = str(rownr)+' / '+str(colnr)
#bn.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
bn.grid(row=rownr, column=colnr, padx="10",pady="10")
bn.config(foreground = "blue" )
bn.config(background = "red") #"#FF0000"
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("300x300")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
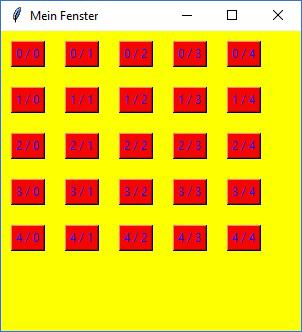
Ergebnis des 1. Beispiels |
||||
|
|
||||
| 1. Beispiel (new version) | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
n=5
for i in range(0,n,1):
root.rowconfigure(i, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(i, weight=1) # 1. editor fill
for rownr in range(0,n,1):
for colnr in range(0,n,1):
bn = tkinter.Button(root)
bn["text"] = str(rownr)+' / '+str(colnr)
bn.grid(row=rownr, column=colnr,sticky="NSEW", padx="10",pady="10")
bn.config(foreground = "blue" )
bn.config(background = "red") #"#FF0000"
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("300x300")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
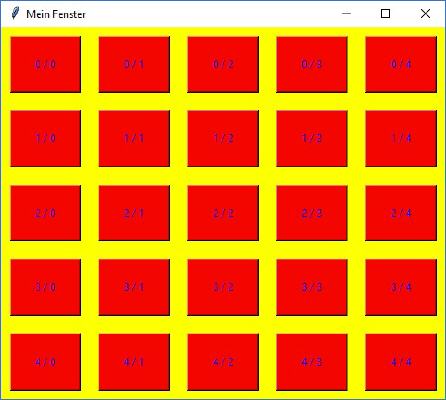
Ergebnis der 1. Beispiels nach der Modifikation |
||||
| 1. Beispiel (new version, different columnweight) | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
n=5
for i in range(0,n,1):
root.rowconfigure(i, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(i, weight=i+1) # 1. editor fill
for rownr in range(0,n,1):
for colnr in range(0,n,1):
bn = tkinter.Button(root)
bn["text"] = str(rownr)+' / '+str(colnr)
bn.grid(row=rownr, column=colnr,sticky="NSEW", padx="10",pady="10")
bn.config(foreground = "blue" )
bn.config(background = "red") #"#FF0000"
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("300x300")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||

Ergebnis der 1. Beispiels nach der Modifikation |
||||
| 1. Beispiel (new version, different columnweight) | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
n=5
for i in range(0,n,1):
root.rowconfigure(i, weight=i+1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(i, weight=1) # 1. editor fill
for rownr in range(0,n,1):
for colnr in range(0,n,1):
bn = tkinter.Button(root)
bn["text"] = str(rownr)+' / '+str(colnr)
bn.grid(row=rownr, column=colnr,sticky="NSEW", padx="10",pady="10")
bn.config(foreground = "blue" )
bn.config(background = "red") #"#FF0000"
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("300x300")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
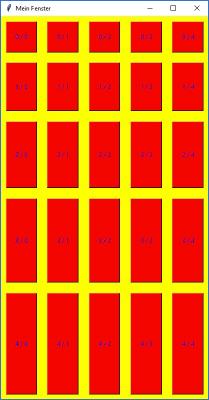
Ergebnis der 1. Beispiels nach der Modifikation |
||||
|
|
||||
| 2. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red") #"#FF0000"
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
#self.label1.grid(row=0, columnspan=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui = tkinter.Entry(root, background="blue", foreground="yellow", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="ew",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name.set("Ihr Name...")
self.inputui["textvariable"] = self.var_name
# ------------------------------------------
self.bnRev = tkinter.Button(root)
self.bnRev["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnRev["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnRev.grid(row=1, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(root)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=1, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name.set( self.var_name.get()[::-1] )
messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("250x150")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
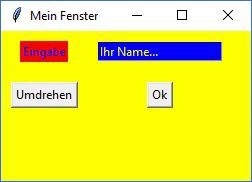
Ergebnis des 2. Beispiels |
||||
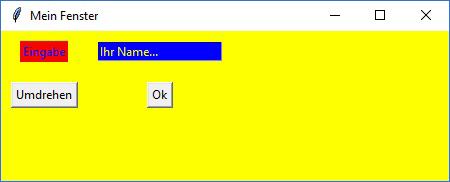
Ergebnis des 2. Beispiels Das Textfeld "wandert" nicht mit, siehe 3. Beispiel |
||||
|
|
||||
| 3. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red")
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name.set("Ihr Name...")
self.inputui["textvariable"] = self.var_name
# ------------------------------------------
buttonframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
buttonframe.config(background = "blue") #"#FF0000"
buttonframe.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=2, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnAction = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnAction["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnAction["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnAction.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=0, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name.set( self.var_name.get()[::-1] )
messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("250x150")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
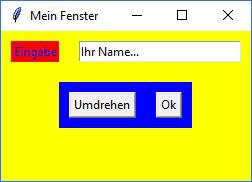
Ergebnis des 3. Beispiels |
||||
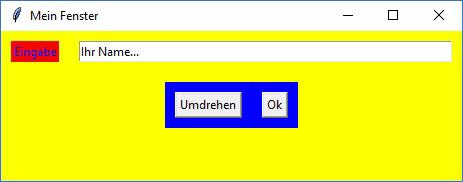
Ergebnis des 3. Beispiels |
||||
|
|
||||
| 4. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=3) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # setzt die 2. Spalte auf fill
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red")
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui1 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui1.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name1 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name1.set("Ihr Nachname...")
self.inputui1["textvariable"] = self.var_name1
self.inputui2 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui2.grid(row=0, column=2,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name2 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name2.set("Ihr Vorname...")
self.inputui2["textvariable"] = self.var_name2
#-------------------------------------------
self.label3 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label3["text"] = "Straße"
self.label3.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label3.config(background = "red")
self.label3.grid(row=1, column=0,sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui3 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui3.grid(row=1, column=1, columnspan=2,sticky="NSEW", padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name3 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name3.set("Strasse...")
self.inputui3["textvariable"] = self.var_name3
# ------------------------------------------
buttonframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
buttonframe.config(background = "blue") #"#FF0000"
buttonframe.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=3, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnAction = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnAction["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnAction["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnAction.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=0, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name1.set( self.var_name1.get()[::-1] )
#messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("350x150")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
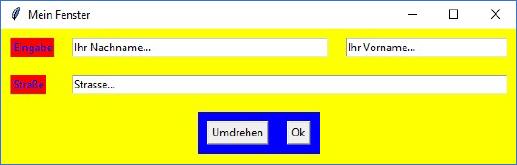
Ergebnis des 4. Beispiels |
||||
|
|
||||
| 5. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=3) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.rowconfigure(2, weight=1) # editor fill
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red")
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui1 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui1.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name1 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name1.set("Ihr Nachname...")
self.inputui1["textvariable"] = self.var_name1
self.inputui2 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui2.grid(row=0, column=2, columnspan=2,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name2 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name2.set("Ihr Vorname...")
self.inputui2["textvariable"] = self.var_name2
#-------------------------------------------
self.label3 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label3["text"] = "Straße"
self.label3.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label3.config(background = "red")
self.label3.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui3 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui3.grid(row=1, column=1, columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name3 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name3.set("Strasse...")
self.inputui3["textvariable"] = self.var_name3
# -------------------------------------------
self.editor = tkinter.Text(root)
self.editor.config(wrap="none") # wrap="word" word char
self.editor.grid(row=2, column=0,columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW", padx="0",pady="0")
sbx = tkinter.Scrollbar(root, orient="horizontal")
sbx.grid(row=3, column=0,columnspan=4, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
sby = tkinter.Scrollbar(root)
sby.grid(row=2, column=3,columnspan=1, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
self.editor["xscrollcommand"] = sbx.set
sbx["command"] = self.editor.xview
self.editor["yscrollcommand"] = sby.set
sby["command"] = self.editor.yview
# ------------------------------------------
buttonframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
buttonframe.config(background = "blue") #"#FF0000"
buttonframe.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=3, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnAction = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnAction["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnAction["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnAction.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=0, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name1.set( self.var_name1.get()[::-1] )
#messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("550x400")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
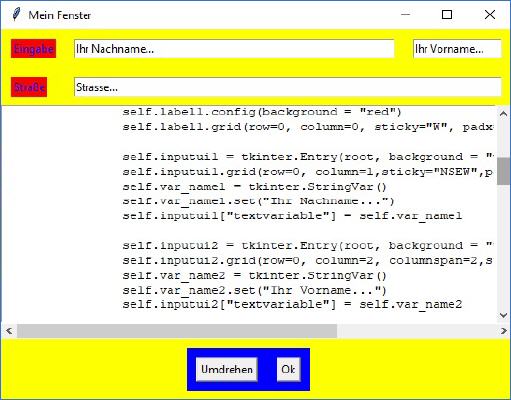
Ergebnis des 5. Beispiels |
||||
|
|
||||
| 6. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
#https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python/python_gui_programming.htm
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=3) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.rowconfigure(2, weight=1) # 1. editor fill
root.rowconfigure(4, weight=10) # 2. editor fill
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red")
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui1 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui1.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name1 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name1.set("Ihr Nachname...")
self.inputui1["textvariable"] = self.var_name1
self.inputui2 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui2.grid(row=0, column=2, columnspan=2,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name2 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name2.set("Ihr Vorname...")
self.inputui2["textvariable"] = self.var_name2
#-------------------------------------------
self.label3 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label3["text"] = "Straße"
self.label3.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label3.config(background = "red")
self.label3.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui3 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui3.grid(row=1, column=1, columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name3 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name3.set("Strasse...")
self.inputui3["textvariable"] = self.var_name3
# -------------------------------------------
self.editor1 = tkinter.Text(root)
self.editor1.config(wrap="none") # wrap="word" word char
self.editor1.grid(row=2, column=0,columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW", padx="0",pady="0")
sbx1 = tkinter.Scrollbar(root, orient="horizontal")
sbx1.grid(row=3, column=0,columnspan=4, sticky="NSEW",padx="20", pady="0")
sby1 = tkinter.Scrollbar(root)
sby1.grid(row=2, column=3,columnspan=1, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
self.editor1["xscrollcommand"] = sbx1.set
sbx1["command"] = self.editor1.xview
self.editor1["yscrollcommand"] = sby1.set
sby1["command"] = self.editor1.yview
# -------------------------------------------
self.editor2 = tkinter.Text(root)
self.editor2.config(wrap="none") # wrap="word" word char
self.editor2.grid(row=4, column=0,columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW", padx="0",pady="0")
sbx2 = tkinter.Scrollbar(root, orient="horizontal")
sbx2.grid(row=5, column=0,columnspan=4, sticky="NSEW", padx="20",pady="0")
sby2 = tkinter.Scrollbar(root)
sby2.grid(row=4, column=3,columnspan=1, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
self.editor2["xscrollcommand"] = sbx2.set
sbx2["command"] = self.editor2.xview
self.editor2["yscrollcommand"] = sby2.set
sby2["command"] = self.editor2.yview
# ------------------------------------------
buttonframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
buttonframe.config(background = "blue") #"#FF0000"
buttonframe.grid(row=6, column=0, columnspan=3, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnAction = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnAction["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnAction["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnAction.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=0, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name1.set( self.var_name1.get()[::-1] )
#messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("550x700")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
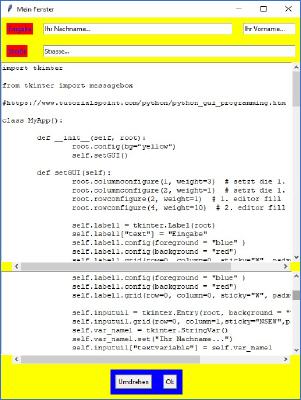
Ergebnis des 6. Beispiels |
||||
|
|
||||
| 7. Beispiel | ||||
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
#https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python/python_gui_programming.htm
class MyApp():
def __init__(self, root):
root.config(bg="yellow")
self.setGUI()
def setGUI(self):
# Columns: auto weight=3 weight=1 auto weight=1 auto
# editor
root.columnconfigure(1, weight=3) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
root.rowconfigure(2, weight=1) # 1. editor fill
self.label1 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label1["text"] = "Eingabe"
self.label1.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label1.config(background = "red")
self.label1.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui1 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui1.grid(row=0, column=1,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name1 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name1.set("Ihr Nachname...")
self.inputui1["textvariable"] = self.var_name1
self.inputui2 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui2.grid(row=0, column=2, columnspan=2,sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name2 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name2.set("Ihr Vorname...")
self.inputui2["textvariable"] = self.var_name2
#-------------------------------------------
self.label3 = tkinter.Label(root)
self.label3["text"] = "Straße"
self.label3.config(foreground = "blue" )
self.label3.config(background = "red")
self.label3.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="W", padx="10",pady="10")
self.inputui3 = tkinter.Entry(root, background = "white", relief=tkinter.SUNKEN)
self.inputui3.grid(row=1, column=1, columnspan=3, sticky="NSEW",padx="10",pady="10")
self.var_name3 = tkinter.StringVar()
self.var_name3.set("Strasse...")
self.inputui3["textvariable"] = self.var_name3
# -------------------------------------------
editorframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
editorframe.config(background = "#00FF44") #"#FF0000"
editorframe.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=3,sticky="NSEW", padx="10",pady="10")
editorframe.columnconfigure(0, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
editorframe.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # setzt die 1. Spalte auf fill
editorframe.rowconfigure(0, weight=1) # 1. editor fill
self.editor1 = tkinter.Text(editorframe)
self.editor1.config(wrap="none") # wrap="word" word char
self.editor1.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="NSEW", padx="0",pady="0")
sby1 = tkinter.Scrollbar(editorframe)
sby1.grid(row=0, column=1, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
sbx1 = tkinter.Scrollbar(editorframe, orient="horizontal")
sbx1.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=2, sticky="NSEW",padx="20", pady="0")
self.editor1["xscrollcommand"] = sbx1.set
sbx1["command"] = self.editor1.xview
self.editor1["yscrollcommand"] = sby1.set
sby1["command"] = self.editor1.yview
# -------------------------------------------
self.editor2 = tkinter.Text(editorframe)
self.editor2.config(wrap="none") # wrap="word" word char
self.editor2.grid(row=0, column=2, sticky="NSEW", padx="0",pady="0")
sby2 = tkinter.Scrollbar(editorframe)
sby2.grid(row=0, column=3,columnspan=1, sticky="NSEW",pady="0")
sbx2 = tkinter.Scrollbar(editorframe, orient="horizontal")
sbx2.grid(row=1, column=2,columnspan=2, sticky="NSEW",padx="20", pady="0")
self.editor2["xscrollcommand"] = sbx2.set
sbx2["command"] = self.editor2.xview
self.editor1["yscrollcommand"] = sby2.set
sby2["command"] = self.editor2.yview
# ------------------------------------------
buttonframe = tkinter.Frame(root)
buttonframe.config(background = "blue") #"#FF0000"
buttonframe.grid(row=6, column=0, columnspan=3, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnAction = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnAction["text"] = "Umdrehen"
self.bnAction["command"] = self.onReverse
self.bnAction.grid(row=0, column=0, padx="10",pady="10")
self.bnOk = tkinter.Button(buttonframe)
self.bnOk["text"] = "Ok"
self.bnOk["command"] = root.quit
self.bnOk.grid(row=0, column=1, padx="10",pady="10")
# ------------------------------------------
def onReverse(self):
self.var_name1.set( self.var_name1.get()[::-1] )
#messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World")
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Mein Fenster")
root.geometry("850x400")
app = MyApp(root)
root.mainloop()
|
||||
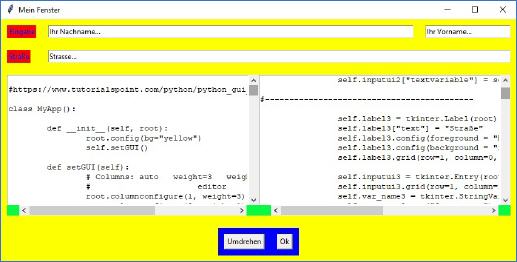
Ergebnis des 7. Beispiels |
||||
|
savedialog Standard Rahmen |
||||
|
|
||||